It is a chronic non-communicable disease that, according to statistics, affects several percent of the total population, psoriasis, with symptoms such as focal rash, itching, and intense peeling of the skin.
The disease can develop at any age, regardless of the social environment to which a person belongs. Psoriasis occurs in both men and women. The disease most commonly affects young people under the age of twenty.
Many people are interested in the question, “Is psoriasis itching, what are its symptoms and treatment, and most importantly: infectious? ” Itching in psoriasis is found in almost 85% of cases, but the disease is not contagious at all. and does not spread by airborne droplets or household appliances. It is difficult to treat, but complex therapy almost always produces good results.
Manifestation of the disease
How does psoriasis manifest itself and what is it? Psoriasis plaques often develop first in areas that are subject to the most friction, such as the elbow or knee.
Signs of psoriasis can appear in absolutely any area of the skin — on the head, face, back, abdomen, palms, legs, armpits, and even the genitals.
If we look at another similar disease - eczema - it affects the inside of the flexor surfaces, with psoriasis - the outside of the knee and elbow joints.
Pathology is chronic and fluctuating, meaning that a person's condition can improve or, on the contrary, be exacerbated by negative factors, while remission and exacerbation are usually completely spontaneous.
Relapse can be caused by alcohol consumption, stress, infectious diseases. The severity of psoriasis during the course of the disease varies from person to person and even from person to person.
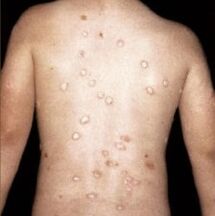
The main symptoms of psoriasis of the skin are plaques, which appear as minor lesions in certain areas. In some cases, they can cover the whole body.
Psoriasis progresses over time, especially if appropriate measures are not taken to remedy it. The progression of the disease consists in an increase in the periods of exacerbations and an increase in the area of the lesion, involving healthy areas of the skin in the inflammatory process. There are cases where the disease continued continuously without periods of remission.
Pathologies such as onychodystrophy - damage to the nail - are very common. This disease can continue on its own without adding a skin lesion. In addition, psoriasis can contribute to the inflammatory process in the joints - psoriasis arthritis (a disease of the lower joints and small joints of the hand) and onychodystrophy can be seen in about 15% of patients with psoriasis.
There are many different ways to treat this disease, but the tendency for the disease to recur and get worse is very difficult to treat. Complete recovery is almost impossible, meaning it remains with the person for the rest of his life, but with proper treatment and adherence to all medical prescriptions, longer remission can be achieved.
Causes
Today, medicine does not know the real cause of this pathology, but it has been shown that immune system dysfunction, neurological disorders, and metabolic disorders can cause the disease. There are several factors that can cause the disease to develop:
- Genetic predisposition,in other words, simple inheritance. Experts say signs of psoriasis can be found in people whose blood relatives have suffered from psoriasis. Moreover, if one parent is ill, the risk of developing the disease increases to 20%, and if both parents - up to 50%. This is due to the existence of certain genes that are responsible for the development of dermatological changes. The first signs of hereditary psoriasis usually appear before 25 years of age.
- Neurological disorders.Any emotional shock, nervous strain, chronic fatigue can cause the disease. In addition, in people with psoriasis, any stressful situation can trigger a worsening of the disease.
- Hormonal failure.Any abnormal changes in the function of the organs of the endocrine system can trigger the mechanism of the disease.
- Violation of the metabolic process.Metabolic disorders due to a lack of useful trace elements and vitamins in the body can cause psoriasis.
- helminthic invasion.Certain types of parasites can provoke disease. Numerous laboratory tests were performed, the results of which showed that many patients with psoriasis were infected with giardiasis, opisthorchiasis, ascariasis, enterobiasis. The situation is that in their vital activities, helminths emit toxic substances that poison the whole body. This leads to exacerbation of chronic diseases and a significant decrease in immunity.
- Viral infectionsthat also attack the human immune system.
From the above, it becomes clear that the process of developing psoriasis is, in one way or another, accompanied by disturbances in the work of the body's defense mechanisms. Psoriasis in the body can trigger a full complex of triggers, or by factors such as an unbalanced diet, climate change, alcohol consumption, and smoking.
Clinical picture and types of psoriasis
How does psoriasis start? The first symptoms of the disease are the appearance of reddish plaques and scaly patches that appear itchy and lichen. Over time, the spots peel off, with a denser scaly layer beneath them.
When the disease begins to progress, a so-called Kenber phenomenon is observed when plaques appear at the site of skin trauma (wounds, cuts, burns).
Varieties
There are several types of psoriasis, each with a specific clinical picture:
- plaque (true psoriasis)is the most common form of the disease, occurring in more than 80% of all patients. The skin is inflamed, dry and thickened, with areas rising above it that are covered with light silvery scales. The skin in these areas is hot to the touch and constantly peeling. After peeling, there are reddish inflammatory foci that are very often damaged and bleed. Inflammation can form large foci. With psoriasis of the elbows and knees, exfoliation is not so pronounced.
- Drop-shaped- There are many small, red or purple, rounded inflammations that rise above the surface of the skin. Guttate psoriasis covers large areas of the body. The first signs of the disease may be after a previous sore throat or pharyngitis caused by a streptococcal infection.
- pustularis the most complex form of the disease. It looks like foci of blistering rashes rising above the surface of healthy skin. These bubbles are filled with exudate. The skin around the pustules turns red, swells, thickens and then peels off. When a secondary infection is associated, the bladders are filled with purulent fluid. Typically, this psoriasis is limited and affects specific areas such as the lower leg and forearm. In severe cases, the inflammation spreads to the surface of the skin and the spots on the rash merge into one focus.
- Psoriatic arthritis- joints and connective tissues are involved in the pathological process. The main manifestation of this form is severe itching. In addition, the skin of the finger joints will be painful, swollen, peeling and peeling.
- oncodystrophy (nail psoriasis)may seem like mycosis. With this disease, the appearance of the nails changes, they become brittle and scaly, and the color of the nail bed and the plate itself can turn yellow or gray. White spots, dots, and transverse lines also appear on and under the nails. The skin under and around the nail becomes tight. Very often, onychodystrophy leads to the loss of nails.
Other symptoms of psoriasis include:
- bleeding wounds (at the site of skin trauma);
- nail erosion;
- intense itching;
- fever, swelling, and joint pain in psoriatic arthritis (not always).
How the disease progresses
There are several stages in the course of the disease:
- Progressive.This is the initial stage of the disease. It is characterized by exacerbations in which the number of new rashes increases.
- Fixed.At this stage, the picture of the disease remains unchanged, meaning that the rash and other symptoms of psoriasis do not increase or decrease.
- Regression phase.The last stage of the disease, which goes without rashes.
Depending on the prevalence of the inflammatory process, the disease may include:
- limited- small areas of skin are affected;
- common- large areas of skin are affected;
- generalized- affects almost the entire surface of the body.
Among other things, psoriasis is a seasonal disease, meaning that all symptoms worsen depending on the season. Most people usually get worse in winter or summer. For some patients, this process does not involve a change of season.
Diagnostics
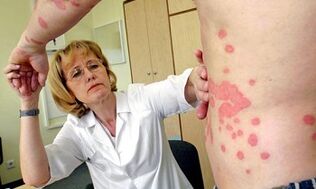
How is this disease diagnosed? The diagnosis of psoriasis is based primarily on an examination by a dermatologist. The examination reveals the shape and extent of the lesion.
In some cases, a differential diagnosis is made to differentiate between psoriasis and another dermatological disease. How to recognize that a patient has this particular disease?
As already mentioned, psoriasis has a Kenber phenomenon that is not characteristic of skin pathologies. Another symptom to consider is when a clear rim appears around a new rim that has not yet begun to peel - a kind of vascular reaction that indicates further progression of the disease.
Sometimes a skin biopsy is used to make the diagnosis more accurate, or tests are performed that can detect the inflammatory process in the blood. You should start treatment immediately after being diagnosed with psoriasis.
Management
Medication
The main therapy is the application of topical preparations in the form of ointments, gels, creams and sprays.
These medications contain ingredients that stop unnecessary cell division in the skin and relieve unpleasant symptoms such as itching. There are several substances that are effective in fighting the disease:
- Glucocorticoid hormones.Relieve inflammation and normalize the immune system.
- Vitamin DVitamin D medications will be most effective when the disease reaches a stagnant stage when the patient's condition is stable. Good results are obtained by taking such drugs in combination with ultraviolet irradiation procedures.
- Silicon.Improves skin condition, has an sorbent effect and absorbs antigens involved in the development of the disease.
- tarhas a good effect on inflammatory foci localized on the head.
- Lecithin.Promotes rapid tissue regeneration. Formulations made with this substance help the body treat inflammation faster.
- Activated Zincremoves redness and relieves itching in a short time.
Patients are also prescribed the following groups of medicines:
- corticosteroids- normalize metabolic processes;
- cytostatics- prevent cell division, but may weaken the body's defense mechanisms;
- Immune modulators- also regulate immune responses, but their effectiveness is questionable;
- non-steroids- relieves inflammation and itching.
Vitamin complexes are prescribed in combination with these drugs.
In addition to medication, the following methods are very popular:
- Hirudotherapy.Leech therapy improves blood circulation and normalizes immune mechanisms.
- Cryotherapy.The special way of "freezing" relieves itching, swelling and inflammation.
- Ultraviolet radiation.These short-term procedures are combined with the introduction of special medications.
Attention!Self-treatment of psoriasis is unacceptable because many drugs have contraindications and are described by a specialist only based on the patient's individual physiological characteristics.

Children usually have less severe psoriasis than adults, so local therapy gives good results, and even in case of exacerbation, long-term remission can be achieved with repeated treatment.
Even if a child is diagnosed with a severe form with appropriate treatment at the right time, the prognosis will be more or less favorable.
The main rule for parents is to get to know the characteristic signs of psoriasis and start fighting this disease right away!
Traditional Medicine
Recipes from traditional medicine are often used to treat psoriasis. Herbal-based compresses will be effective.
Grind 4 tablespoons to prepare for compression. tablespoons dry herb and pour a glass of boiling water and let it cook. The broth in the broth should be moistened and applied to sore spots.
The following plants have healing properties:
- marigold; horseshoe
- ;
- walnut leaves; celandine; yarrow;
- sweet clover; burdock
- ;
- black currant leaves.
You can also make an oral tincture. To do this, 1 tbsp. a spoonful of dry herb should be poured with a glass of boiling water, stick to it for 8 hours, filter and drink 100 ml twice a day, preferably half an hour before meals. Suitable for collecting herbs:
- St. John's wort; celandine;
- sequence;
- marshmallows;
- valerian.
Attention!Some of these herbs can cause side effects, so you should read all the contraindications before starting treatment.

Medicated ointments for home treatment are very popular. Here are some effective recipes:
- Burn the dry rosehips and mix the ashes with Vaseline. Ointment should be applied daily to the affected areas.
- Grind the celandine leaves to make 2 tbsp. spoon, add lanolin and Vaseline. Ointment for the treatment of inflamed skin.
- Mix a series of tinctures with lanolin and Vaseline and rub into psoriatic plaques.
- Grind the root of the meadow root, mix it with oil or Vaseline, bring the resulting ointment to a boil, cool and lubricate the sore spots.
Soothing herbal teas are beneficial. It can be cooked from uterus, oregano, chamomile, mint, thyme, valerian, linden, peony.
Traditional medicine does not guarantee 100% of the result, it is better to combine it with the main treatment.
Psoriasis and pregnancy
Many women with psoriasis who are in a situation are afraid of how the disease will behave during this period.
Psoriasis is an unpredictable disease, so it is difficult to answer the question, "How to determine the course of the disease during pregnancy. "There are cases when the disease completely disappeared after childbirth.
Every pregnant woman worries about whether the disease can spread to her baby, but it’s not the disease itself that is inherited, it’s just a predisposition to it.

During breastfeeding, if the mother is undergoing therapeutic treatment with strong drugs, breastfeeding is very dangerous because the substances can harm the health of the baby. In this case, you must interrupt the treatment or move the baby to artificial feeding.
The disease does not affect fetal conception and intrauterine development, but the medications your mother takes can have negative consequences, so it is important to consult your doctor when planning a pregnancy, some of which will be canceled.
Prevention
This disease cannot be prevented, but its manifestations can be significantly reduced. In order to achieve a reduction in the symptoms of the disease, you must follow the following preventive rules:
- Don’t try to get nervous and learn to control your emotions. Natural sedatives can be used to facilitate this task.
- Reduce your consumption of salty, smoked, spicy, fried and fatty foods, as well as honey, citrus fruits, chocolate and coffee.
- Wear clothes made of natural fabric.
- Choose low-pH body care products that do not dry out or irritate sore skin.
- Be careful with medications, as many of them can cause psoriasis to flare up, antibiotics are especially dangerous.
- Quit smoking and alcohol.
- Avoid direct sunlight.
Psoriasis is one of the most common skin conditions, the nature of which is still not fully understood. The disease causes a lot of discomfort, worsens the quality of life and reduces a person’s self-esteem.
This can happen suddenly and unfortunately no one is free from this disease. Therefore, it is very important to know how this pathology manifests itself so that you can see a doctor in time and start treatment.























